The Importance of Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in Product Development
Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a buzzword in the world of product development. It is a product with just enough features to satisfy early customers and provide feedback for future product development. MVP is a core component of the Lean Startup methodology, which aims to develop businesses through iterative and validated learning. In this article, we will explore the concept of MVP, its core features, target customers, and its importance in product development.
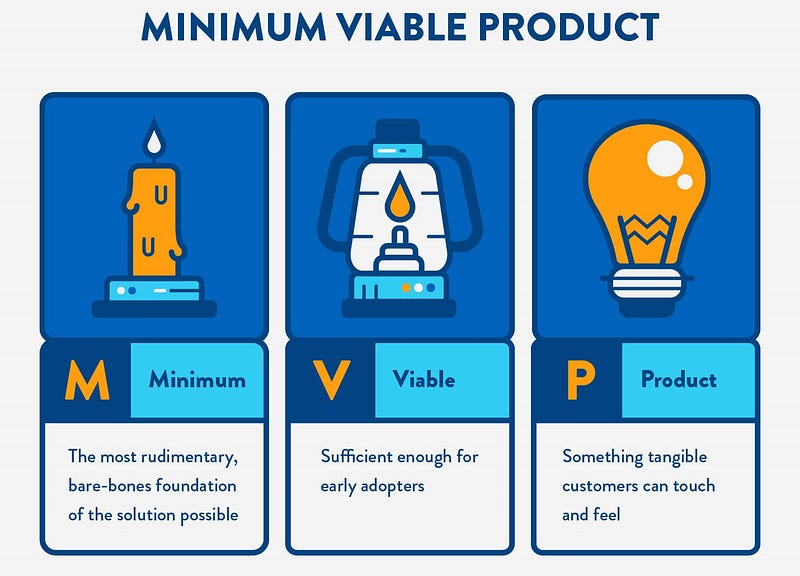
Core Features of MVP
The core features of MVP are the minimum set of features required to deliver value to early customers. The MVP should be a working product that demonstrates the basic functionality of the final product. The MVP should be designed to be delivered to early customers as soon as possible to gather feedback and validate the product hypothesis. By getting the product to early customers, the development team can accelerate learning, reduce wasted engineering hours, and establish the builder’s abilities in crafting the required product.
Target Customers for MVP
The target customers for MVP are early adopters who are willing to test the product and provide feedback. These early adopters are typically risk-takers who are excited about new products and technologies. They are the customers who are most likely to give honest feedback on the product and help the development team identify any areas of improvement.
Lean Startup Methodology and MVP
The Lean Startup methodology is a business development approach that aims to create a product or service through iterative and validated learning. MVP is a core component of the Lean Startup methodology. The methodology involves testing a product hypothesis with minimal resources, getting the product to early customers as soon as possible, and iterating based on the feedback received.
Contrasting MVP with Traditional Product Development Methods
In traditional product development methods, the focus is on delivering a fully-featured product that meets all customer requirements. This can take months or even years, and the cost of development can be high. MVP, on the other hand, focuses on delivering a product with only the core features required to deliver value to early customers. This approach can significantly reduce development time and costs, while also validating the product hypothesis.
Importance of MVP in Validating Business Ideas and Reducing Costs
MVP is essential in validating business ideas and reducing costs. By testing the product hypothesis with an MVP, businesses can gather feedback from early customers, identify areas of improvement, and iterate based on the feedback received. This approach can significantly reduce the cost of development, as it focuses on delivering only the core features required to deliver value to early customers.
Example of MVP
One example of an MVP is the Rippa robot developed by the University of Sydney. The robot was developed to test the hypothesis that a robot could be used to remove weeds from crop fields. The MVP was designed to be low-cost and easy to build, and it was tested in a real-world environment. The feedback received from early customers was used to improve the design of the robot, leading to the development of a fully-featured product that met all customer requirements.
Importance of Testing in MVP
Testing is crucial in MVP, as it helps businesses identify any issues with the product and gather feedback from early customers. By testing the product with early customers, businesses can identify areas of improvement and iterate based on the feedback received. Testing can also help businesses evaluate the financial viability of the product idea, ensuring that the product meets the needs of the target market.
Benefits of Testing
The benefits of testing include identifying any issues with the product, gathering feedback from early customers, and evaluating the financial viability of the product idea. Testing can also help businesses identify areas of improvement, leading to the development of a fully-featured product that meets all customer requirements.